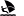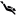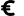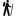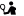The long beach in Rapaniana is located 20km west of Chania and 4km east of Kolimbari. It is just a part of the vast beach stretching from Cape Rodopos to Chania, including the beaches in front of Skoutelonas, Minothiana and Rapaniana villages.
At the point where the prefecture of Rethymno meets Chania, east of Georgioupolis beaches, we find the beaches of Kavros and Kournas. The place at its greatest part is developed and only a very small part of it has been left untouched. Between this remaining virgin parts of the beach there is an extensive and very important ecosystem of dunes.
Ierapetra is located 35km southeast of Agios Nikolaos and is the southernmost city of Greece. It is built in one of the warmest areas of Crete, which makes it very popular for holidays, even until the end of autumn. The wider area of Ierapetra is famous for its beaches, stretching along a vast beachfront. Almost all of them are covered by the characteristic fine black pebbles, which do not stick in the leg, and the sea is usually flat.
Istro(n) is located 12km east of Agios Nikolaos and 22km north of Ierapetra, very close to Kalo Chorio. It is a quiet village, situated in a lush valley full with olive groves and springs, which has been developed during the last decades. However, the development was fortunately mild, mainly due to the regional building restrictions because of the archaeological discoveries. The main growth driver of Istron is undoubtedly the emerald beaches which are scattered in three adjacent bays.
The east end of the long Ierapetra beach is called Livadia, and beyond this, is called Peristeras. This is a secluded area with high cliffs surrounding it. The beach is sandy and has several smooth rocks in places. You can reach the easternmost part of Saint Andrew by walking from the road. However, there is a second sandy beach in Peristeras, just behind the rocky end of the long beach, that can be accessed by the road. This is very well protected by prying eyes, but there are many rocks.
The peninsula of Grammeno(s) is located 85km south of Chania and 5km east of Paleochora, on the road connecting Paleochora with Koudoura. Koudoura is a warm area with greenhouses, where most citizens of the area work.
Lagoufa is located right after the east end of Makrigialos main beach, around 59km southeast of Agios Nikolaos and 24km east of Ierapetra. It consists of two adjacent protected coves, which are formed near the big hotels of Makrigialos.
Vathianos River empties in the area, but it gets dry on the summer. The area has several adjacent coves with gold sand and shallow waters. Because the beach front is facing north, waves are quite common. That's why in some places you will see several small piers, breaking the waves.