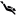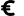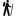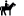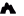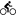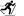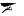Milatos Cave, also known as Rapas cave, is located 3km northeast of Milatos at an altitude of 155m. In order to reach the cave, the visitor should drive 2.5km east of Milatos (following the road sings) and then walk in the uphill footpath that leads to the cave entrance (10-15 minutes walking). Cave is easily accessible, is open to visitors, but torches are necessary for those who want to see the darker points of the cave.

One Turk from Voulismeni, called Terzalis or Nteres, informed Hassan Pasha that the inhabitants were hiding in Milatos cave and his lieutenant, Hussein Vei, arrived with 5000 soldiers to force the Christians come out. 150 Christian chieftains kept away Hussein, causing several damages to his troops. However, the Turks succeeded to surround the cave entrance, but Greeks were resisting successfully.
The siege began on February 3 and lasted several days. The besieged Greeks had to face thirst, hunger and odor from corpses of elder dying. It is also said that 40 children were born in the cavern during the days of siege. Turks installed cannons on the opposite hills and began bombing the cave. Cretans put duvets and mattresses around the cave, to absorb the force of the cannon balls. At the same time they were waiting for help. Indeed, 2500 Greeks from other places of Crete arrived to assist, however Turks had occupied strategic positions and they were more.
Turks invited the besieged habitants to surrender, swearing that they will not touch them. Greeks did not trust them and refused to come out. On February 15, Turks set fire near the entrance of the cave, filling it with smoke. The suffocating atmosphere forced Greeks to exit the cave. The first that came out were the defenders. Turks, despite the initial reassurances of Hassan Pasha, massacred 30 warriors. Turks captured the habitants, tied them with ropes and chains and moved them to Neapolis. Women were tied with their braids and the most beautiful girl was given as slave to Pasha.
Elderly men were moved to the position “Grambelles”, where cavalry passed and trampled them. Turks cut their heads and created a pyramid with them. All infants were massacred and their mothers were sold as slaves. 18 parsons were either massacred or burnt alive, after cutting their 3 fingers, which they crossed. This was the end of the drama in the cavern of Milatos.
Notably, Hassan Pasha earned the wages of sin for his crimes in Lassithi Plateau and Milatos in the following days. After leaving Milatos, the troops encamped in Kastelli, before proceeding towards Messara plain. But while Hashan was riding in the plain of Kastelli, his horse bolted, he fell down and he was instantly killed. He was then buried near the church of Agios Titos in Heraklion. Historians estimate the number of besieged civilians in 2000 -3700 and 150 to 300 fighters. Other versions tell about 5000 people. However these numbers are considered excessive, as the cave could not hold all these people and the population of the area is estimated in smaller numbers. The actual number may exceed 1000, which anyway is another drama in the history of the Cretan revolutions.
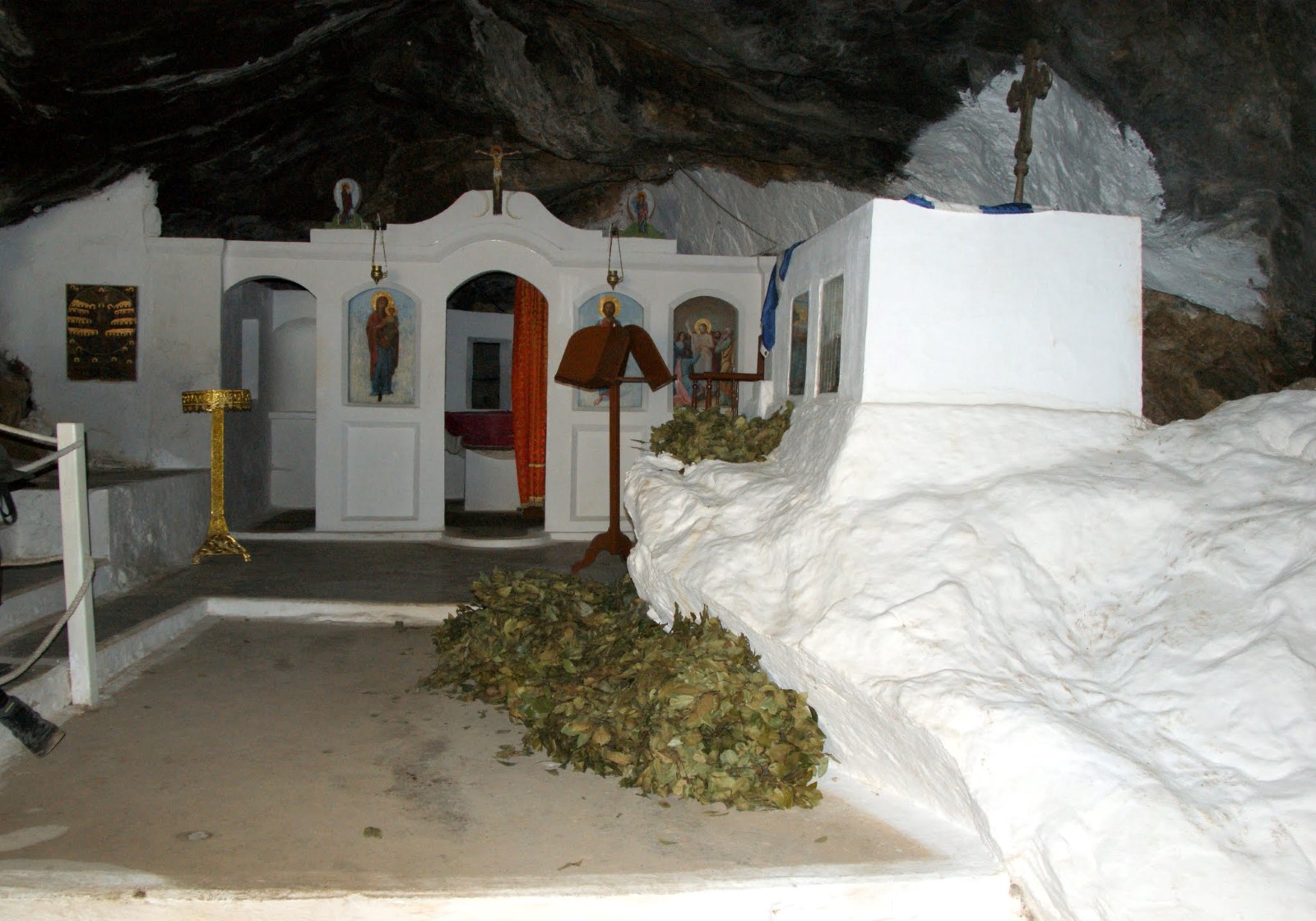
The cave has 8 entrances along a face of 40m. The main entrance has 9m width and 2m height. The rightmost entrance allows the daylight illuminating the room where the chapel of Saint Thomas is built. Both entrances lead to the main part of the cave. On the other hand, the remaining entrances lead to the left part of cave, which is smaller.
In the first hall of the main part of the cavern, locals built in 1935 a chapel dedicated to Apostle Thomas, which celebrates on Saint Thomas Sunday. On the same day, a local fest is celebrated and deads are commemorated. An ossuary is built near the church, containing some bones from the victims of 1823.
The cave consists of many small halls at different levels. In the main part of the cave, near the chapel, the floor descends and turns horizontal later. The cave is full of small and large columns, arranged in rows and dividing the cave into different chambers. Stalagmites are few but spectacular, while stalactites are scarce.
The overall length of the cave is 75m, the width near the entries is 45m and this decreases as you walk inside the cavern. The deepest part of the cave is located 12m below the entry level. Access is easy, but the visitor should bend in a few points. The overall routes inside the cavern approach 200m. At the back of the cave, an altar has been found in a natural cavity. In front of it, archaeologists found ancient graves, human bones and particles of pottery. These findings indicate that the cave has been used as a place for burials.
What is near me?
Additional Info
- Location: Lassithi Prefecture
- Type: Open to visitors, Horizontal Cave
- Length (m): 200
- Accessibility: Walking








 Milatos Cave
Milatos Cave