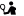The Minoan Kydonia was built at the current location of the old town of Chania. Kydonia was the third largest town of Minoan Crete. Here developed a thriving craft industry and the town became rich through sea trade, which was favored by its position. Indeed, the ancient writers mention Kydonia as the mother of the Cretan towns.
Asfendou cave is located near the village of Sfakia, on a steep slope at position Skordalakia. The road connecting Asfendou with Kallikratis passes nearby and there is a plateau with an area of 2000 square meters in front. Skordoulakia cave is a very small rock shelter without woo much depth that barely fits two people and is located on a hillside at the beginning of the canyon Asfendou.
A living museum of historical memory that is worth seeing by any visitor of Crete that records the suffering of the Greek people during the German Occupation, is the galleries of Platanias. The shelter was built below the church of Agios Dimitrios at Pano Platanias by the requisitioned locals, for the Germans.
Within short distance from Elounda, near the salt pans, we meet few remains of the ancient city Olous (most inside the sea) that was inhabited since the Minoan period. Olous was one of the hundred most important cities of ancient Crete with a maximum population of over 30,000 people.
The archaeological site of Ancient Tylisos is located 16km west of Heraklion, in a strategic location. Tylissos was a Minoan city that was flourished in 1650-1450 mainly because it was amid the road that led from Knossos to the west Minoan centers and Ida Mount. In 1450 it was destroyed, but was rebuilt and prospered until 1200.
Ancient Lissos was the seaport of Elyros and was built in a small valley between Sougia and Paleochora. It flourished from the Hellenistic period up to the 9th century, when it was destroyed by the Saracens. It was famous for the Asclepion, where patients from all over the island arrived to be healed from the thermal baths.
The necropolis of Armeni is situated 9km south of the town of Rethymnon, on the main road which leads to the south coast of Crete. The greatest Late Minoan III A-B (c. 1400-1200 BC) cemetery was discovered on a shallow hill called Prinokefalo, which means “hild of the wild oaks”.
The ancient Itanos was one of the strongest cities in Crete, especially during the Hellenistic and Greco-Roman times. The name comes from its founder Itanos, who came from Phoenicia. Its territory, during its peak, stretched from Cape Samonio (current Cape Sidero) to Cape Erythrae (current Cape Goudouras).