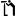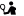Rafioli or Isihakis Mansion is located at the mountainous area of Nerokourou at position Chalometro and is a complex of the Venetian period, with great architectural importance. The area has been declared a historical monument and place of particular natural beauty.
The idyllic suburb of Chania, called Perivolia, till the German Occupation hosted the luxurious villa of Mustafa Naili Pasha, known also as Giritlis (= Cretan), which was destroyed by the Germans in order to use its materials for building their own buildings.
The Tower of St. George was built at the homonym village of Sitia province, which was then called Tourtouli. It was the residence of ordakayasi (Turkish commander) of Sitia, Ibrahim Afentakis or Afentakakis. It was an complete tower with a large courtyard and prisons.
The neighborhood of Palea Roumata called Arhontika (Mansions) took its name after the Venetian mansion, which still survives here, which belonged to the family of Renier. The entrance of the villa has an imposing doorway and a family crest. Nikolaos Renieris (1758-1847), one important Cretan politician came from this family.
Northwest of the village Damania, on the road that heads to Arkadi village (Monofatsi province) we meet the hill of Kefala. Kefala has unique views to Damania and the beautiful dam-lake, the fertile plain of the village and other villages of Monofatsi. The whole area in the upper part of the hill is full of the remains of the village that was there centuries ago and is now completely deserted.
Southeast of the Monastery of St. George Epanosifis, till 1671, there was the settlement of Livadia. The village was a fief of the Patriarchate of Constantinople, which was leased to various lords of the area. Two names of the leasees that have survived in time are George Dalaporta (1332) and Stephen Foscarini (1450).
Between the villages of Ano Varsamonero, Kaloniktis, Ano Malaki and Kato Malaki, at an area full of oaks and ancient olive trees, still stands the ruined Venetian Mansion of Syngelos. Apparently this building was used for controlling and overlooking the region by its owner during the Venetian period or later.
In the area of Akrotiri Cape, near Chania, the Turks had built two towers towards protecting and controlling the wider area. The first was built in Kounoupidiana area (near the Tombs of Venizelos), while the second was built in Sternes position (overlooking Souda Bay). Apart from them, there were several other fortified chateaus, like the tower of Mouzouras.