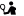Agios Thomas (Saint Thomas) is one of the most impressive mountain villages of Crete. This is mainly due to the rocks of the region that are easy to carve. Excellent monuments of carved architecture travel us to ancient times with carved Minoan presses, Roman tombs and cavernous temples.
At position Grigori Peak by Kamilari we meet the ruins of alarge domed tomb (34m long perimeter) with panoramic sea views. The tomb was discovered in 1959 by the Italian archaeologist Doro Levi, and dates back from 2000 BC.
The historic Monastery of Odigitrias on the way to Agiofaraggo hides many treasures. Beyond the monastery itself with such great history and the tower of Xopateras, it conceals another surprise north of the monastery. This is the prepalatial necropolis of Odigitria, named after the monastery, as we still don’t know the name of the town it belonged to.
The ruins of the largest Minoan cemetery in Crete have been discovered in this area with 252 graves from the early Minoan period, 1800 vases and many artefacts buried with the dead.
The prepalatial cemetery Koumasa is located between Loukia and Koumasa. This Minoan archaeological site was first excavated by Stephanos Xanthoudides from 1904-1906 and four graves came to light (three vaulted graves and one rectangular).
At position Platyskinos near Achladia, Sitia, a large underground vaulted tomb of diameter 4.08m, height 4.16m and corridor 9m, has been revealed. The tomb, extremely rare especially in Eastern Crete, dates back from 1400-1220 BC and is thought to have been inspired by the tombs of Mycenae.
Just next to the small village of Fylaki at Apokoronas province, Chania, you will find the vaulted tomb of Fylaki. It was built in the post Minoan Times. It is very well preserved and clean. There is a long aisle at its entrance and its pyramid-like roof is very impressive.
Above the scenic village of Trialonia, Kissamos district, and a little on the east, we meet the hill of Kefala. Kefala has views to all surrounding areas and hides a truly unknown treasure, a huge archaeological site which has not been protected by the Greek State and is still being destroyed.