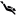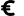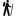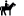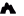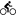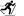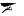Castel del Corner or fort of Paleochora is located on the hill Kastelos south of Katalagari village, at an area full of olive trees and vineyards. According to tradition, it was built by Nicephorus Phocas after the liberation of Crete by the Arabs in 961 AD.
In the Province of Selino (the wider area of Paleochora), in Sougia Koyles were built in the positions Boukelasi, Koustogerako, Kefala in Rodovani (ancient Elyros), Stavros near Kantanos, Moustakos, Spaniako and Vigles. The Koules of Spaniako controlled the valleys, the passages and the towering peaks around it, while on the south lies the Libyan Sea.
The fort, according to a Turkish inscription on its outside walls, was built in 1740-1741. It was presumably founded by an Islamized Venetian nobleman who belonged to the family of Zeni, and was named Tsin Ali or Tzinalis. Tzinalis is a real historical person and was one of the toughest janissaries of Sitia.
The Koules of Spaniakos controlled the valleys, the passages and the towering peaks around it, while on the south lies the Libyan Sea. It had a very important role in the suppression of the revolution of 1866-1869.
Voukolies village is located at the 27th kilometer of the road Chania - Kandanos - Paleochora. It was initially a Turkish village and in 1866 the Turks, in order to consolidate their position, built a strong tower southwest of the village and within half a kilometer from Voukolies.
Fortezza is a suburb of Heraklion, built on a high hill next to the hospital of Venizelion. This hill was ideal for establishing a fortress, as evidenced by its name.
The fort of Liopetro was located in Fatsi position, near the village Hamezi (Sitia province). It is believed to have been built on the site of an older fort, of which the tank survives. Liopetro is built on a steep hill with panoramic views to all sides. Atop of it, there is the scenic chapel of Prophet Elias and the remains of walls, tanks and other buildings.
The fort was built by Pescatore in 1206, who named it Nuovo (i.e. New), probably because it was one of the fortresses he built from scratch, without another preexisting. It is believed that this is the site of the ancient city Aina. The entrance to the fort was located on the south side of the hill, where there was a steep staircase.