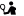Knossos was the most important city on Crete before the Roman Era and the center of the first brilliant European civilization, the Minoan. The palace of King Minos is the most visited archaeological site in Crete with more than 1.000.000 visitors per year.
Rousolakos is located 91km southeast of Agios Nikolaos, right next to the beach of Hiona. Here, the archaeologists have discovered an important town of Minoan Crete covering an area of more than 50 acres, which flourished particularly at the end of the Minoan Age till 1450BC.
The archaeological site of Malia is located 3km east of Malia, next to the wetland of the area and very close to the beach. It was an important Minoan city and housed the third largest Minoan palace, after Knossos and Phaestus. According to mythology, Sarpedon reigned here, who was brother of Minos and son of Zeus and Europa. Sarpedon was expelled by his brother Minos and then took refuge in Lycia in Asia Minor.
The archaeological site of Gournia is located on a hill west of Pachia Ammos, near the road connecting Agios Nikolaos to Ierapetra, 19km east of Agios Nikolaos. The city flourished in the Minoan period and is the most complete excavated Minoan town in Crete. Because of its good conservation, it was named as the "Pompeii of Crete". The excavation of Gournia was implemented by an American Archaeology Group, headed by Harriet Boyd, in 1901-1904.
Phaestus (Phestos or Festos) was a Minoan city on Crete, the ruins of which are located 55km south of Heraklion. The city was already inhabited since 6000BC and prospered concurrently with the city of Knossos, till the 1st century BC.
The Minoan Kydonia was built at the current location of the old town of Chania. Kydonia was the third largest town of Minoan Crete. Here developed a thriving craft industry and the town became rich through sea trade, which was favored by its position. Indeed, the ancient writers mention Kydonia as the mother of the Cretan towns.
The archaeological site of Ancient Tylisos is located 16km west of Heraklion, in a strategic location. Tylissos was a Minoan city that was flourished in 1650-1450 mainly because it was amid the road that led from Knossos to the west Minoan centers and Ida Mount. In 1450 it was destroyed, but was rebuilt and prospered until 1200.
The necropolis of Armeni is situated 9km south of the town of Rethymnon, on the main road which leads to the south coast of Crete. The greatest Late Minoan III A-B (c. 1400-1200 BC) cemetery was discovered on a shallow hill called Prinokefalo, which means “hild of the wild oaks”.